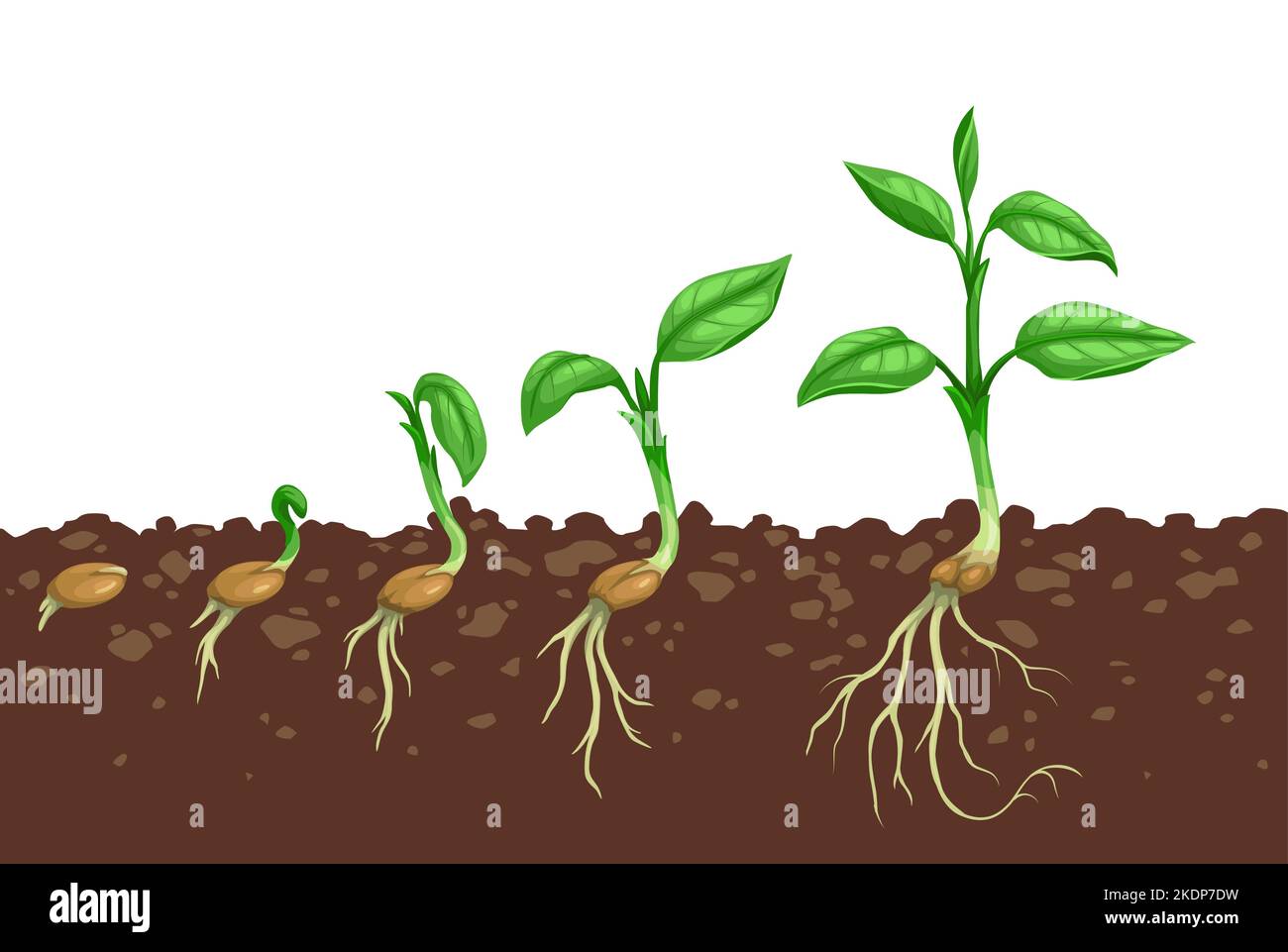
The concept of seed and sapling plays a crucial role in understanding the growth and development of plants, ecosystems, and even human endeavors. Whether you're a gardener, environmentalist, or someone curious about nature, grasping the significance of seeds and saplings is essential. This article delves into the intricacies of seed and sapling, exploring their roles in nature and beyond.
From ancient civilizations to modern science, humans have long recognized the importance of seeds and saplings. These tiny beginnings hold the potential for life, growth, and sustainability. By understanding the processes involved in seed germination and sapling development, we can better appreciate the natural world and its interconnected systems.
In this article, we will explore the science behind seed and sapling, their ecological significance, and how they impact our daily lives. Whether you're planting a garden or studying environmental science, this guide will provide valuable insights into the world of seeds and saplings.
Read also:Walts Center Lanes A Timeless Bowling Haven
Table of Contents
- What Are Seeds and Saplings?
- The Science of Seed Germination
- Stages of Sapling Development
- Importance of Seeds and Saplings
- Benefits for Ecosystems
- Challenges Facing Seeds and Saplings
- Sustainable Practices for Seed and Sapling Care
- Seed and Sapling in Agriculture
- Urban Gardening with Seeds and Saplings
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What Are Seeds and Saplings?
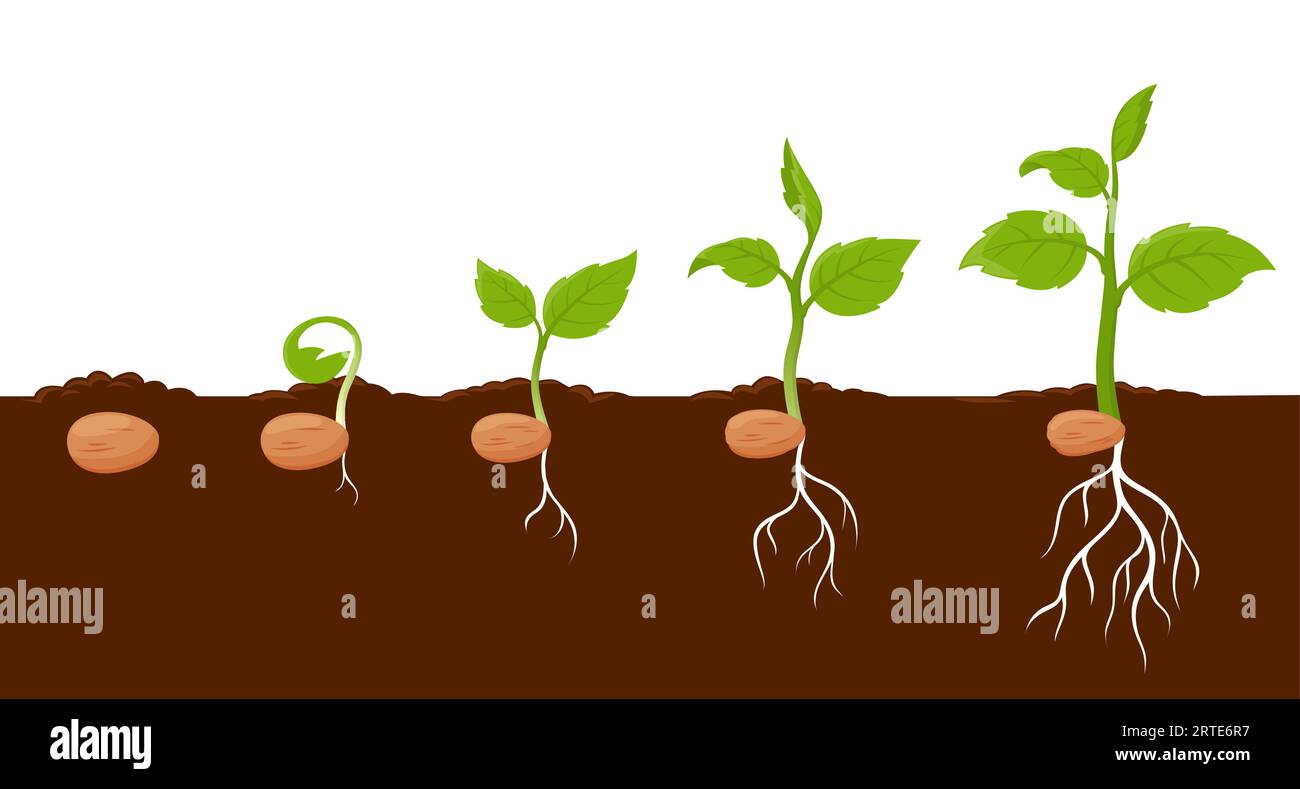
Seeds and saplings represent the early stages of plant life. A seed is a small embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, designed to germinate and grow into a mature plant. Saplings, on the other hand, are young trees that have emerged from seeds and are in the process of developing into full-sized trees.
The lifecycle of a plant begins with a seed, which contains all the genetic information needed for growth. Once conditions are favorable, the seed germinates, and a sapling emerges. This stage is critical, as it determines the plant's future health and productivity.
Characteristics of Seeds and Saplings
- Seeds are compact, durable, and often resistant to adverse conditions.
- Saplings require specific environmental conditions to thrive, such as adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients.
- Both seeds and saplings play vital roles in maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
The Science of Seed Germination
Seed germination is a fascinating biological process where a seed transforms into a living plant. This process involves several stages, including imbibition, where the seed absorbs water, and the activation of enzymes that break down stored nutrients.
Temperature, moisture, and oxygen levels are key factors influencing seed germination. For example, studies show that seeds germinate best at temperatures between 20°C and 30°C, depending on the species. Additionally, the presence of light or darkness can also affect germination, depending on the plant's requirements.
Factors Influencing Germination
- Water: Essential for activating metabolic processes within the seed.
- Temperature: Optimal temperatures vary by species but are crucial for enzyme activity.
- Oxygen: Required for respiration during germination.
- Light: Some seeds require light for germination, while others do not.
Stages of Sapling Development
After germination, the seedling grows into a sapling, which undergoes several developmental stages. These stages include root establishment, shoot growth, and leaf development. Each stage contributes to the sapling's ability to survive and thrive in its environment.
During root establishment, the sapling develops a strong root system to anchor itself and absorb water and nutrients. Meanwhile, shoot growth focuses on extending upward toward the light, while leaf development ensures photosynthesis can occur efficiently.
Read also:Unveiling The Allure Of Spindles On Remsen A Detailed Exploration
Key Milestones in Sapling Development
- Root establishment: Critical for stability and nutrient absorption.
- Shoot growth: Facilitates access to sunlight and air.
- Leaf development: Enables efficient photosynthesis and energy production.
Importance of Seeds and Saplings
Seeds and saplings are vital components of ecosystems worldwide. They contribute to biodiversity, provide food and shelter for wildlife, and support human livelihoods through agriculture and forestry. Understanding their importance helps us appreciate the interconnectedness of all living things.
Moreover, seeds and saplings play a significant role in combating climate change. Trees, which begin as seeds and saplings, absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate the effects of global warming. This makes seed conservation and sapling care essential for environmental sustainability.
Ecological and Economic Benefits
- Seeds and saplings contribute to biodiversity and habitat creation.
- They provide resources for food, medicine, and materials.
- Planting seeds and nurturing saplings helps combat deforestation and climate change.
Benefits for Ecosystems
The presence of seeds and saplings enriches ecosystems in numerous ways. They serve as food sources for animals, create habitats for various species, and enhance soil fertility through nutrient cycling. Furthermore, they play a crucial role in maintaining water cycles and preventing soil erosion.
Research indicates that healthy seed and sapling populations are indicators of robust ecosystems. For instance, a study published in Ecological Applications found that diverse seed banks contribute significantly to ecosystem resilience and recovery after disturbances.
Contributions to Ecosystem Health
- Provide food and shelter for wildlife.
- Enhance soil fertility and structure.
- Support water cycles and prevent erosion.
Challenges Facing Seeds and Saplings
Despite their importance, seeds and saplings face numerous challenges in today's world. Climate change, deforestation, and habitat destruction threaten their survival. Additionally, invasive species and pests can disrupt natural processes, affecting seed germination and sapling growth.
Conservation efforts are vital to protecting seeds and saplings. By implementing sustainable land management practices and supporting reforestation initiatives, we can help ensure their continued existence and contribution to ecosystems.
Addressing Threats to Seeds and Saplings
- Combat climate change through carbon reduction strategies.
- Protect natural habitats from deforestation and degradation.
- Control invasive species and manage pest populations.
Sustainable Practices for Seed and Sapling Care
Adopting sustainable practices is essential for preserving seeds and saplings. Techniques such as seed banking, agroforestry, and organic gardening promote their health and longevity. These methods focus on minimizing environmental impact while maximizing benefits for both plants and people.
For example, seed banking involves collecting and storing seeds under controlled conditions to preserve genetic diversity. Agroforestry integrates trees into agricultural landscapes, enhancing productivity and sustainability. Organic gardening practices prioritize natural fertilizers and pest control methods, reducing chemical use.
Implementing Sustainable Practices
- Establish seed banks to preserve genetic diversity.
- Practice agroforestry to integrate trees into farming systems.
- Use organic gardening techniques to promote plant health.
Seed and Sapling in Agriculture
In agriculture, seeds and saplings are foundational to food production. Farmers rely on high-quality seeds and healthy saplings to grow crops and maintain productivity. Advances in agricultural science have improved seed selection and sapling care, leading to increased yields and resilience.
Genetic engineering and biotechnology have also played a role in enhancing seed and sapling performance. However, these technologies must be balanced with ethical considerations and environmental sustainability to ensure long-term benefits.
Advancements in Agricultural Practices
- Improved seed varieties for higher yields and disease resistance.
- Advanced sapling care techniques for better growth and productivity.
- Incorporating technology to optimize agricultural practices.
Urban Gardening with Seeds and Saplings
Urban gardening has gained popularity as people seek to connect with nature and grow their food in cities. Seeds and saplings are central to this movement, offering opportunities for individuals to cultivate plants in limited spaces such as balconies, rooftops, and community gardens.
By growing seeds and nurturing saplings, urban gardeners contribute to local biodiversity, improve air quality, and promote mental well-being. These efforts also foster a sense of community and shared responsibility for the environment.
Tips for Urban Gardening
- Choose appropriate seeds and saplings for your space and climate.
- Utilize vertical gardening techniques to maximize space.
- Engage with local gardening groups for support and knowledge sharing.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, seeds and saplings are indispensable components of our natural world. Their roles in ecosystems, agriculture, and urban gardening highlight their importance in sustaining life and promoting environmental health. By understanding and supporting their growth, we can contribute to a more sustainable future.
We invite you to take action by exploring seed and sapling care in your own life. Whether you're planting a garden, supporting conservation efforts, or learning more about sustainable practices, every step counts. Share this article with others and join the conversation about preserving our planet's natural resources. Together, we can make a difference.